

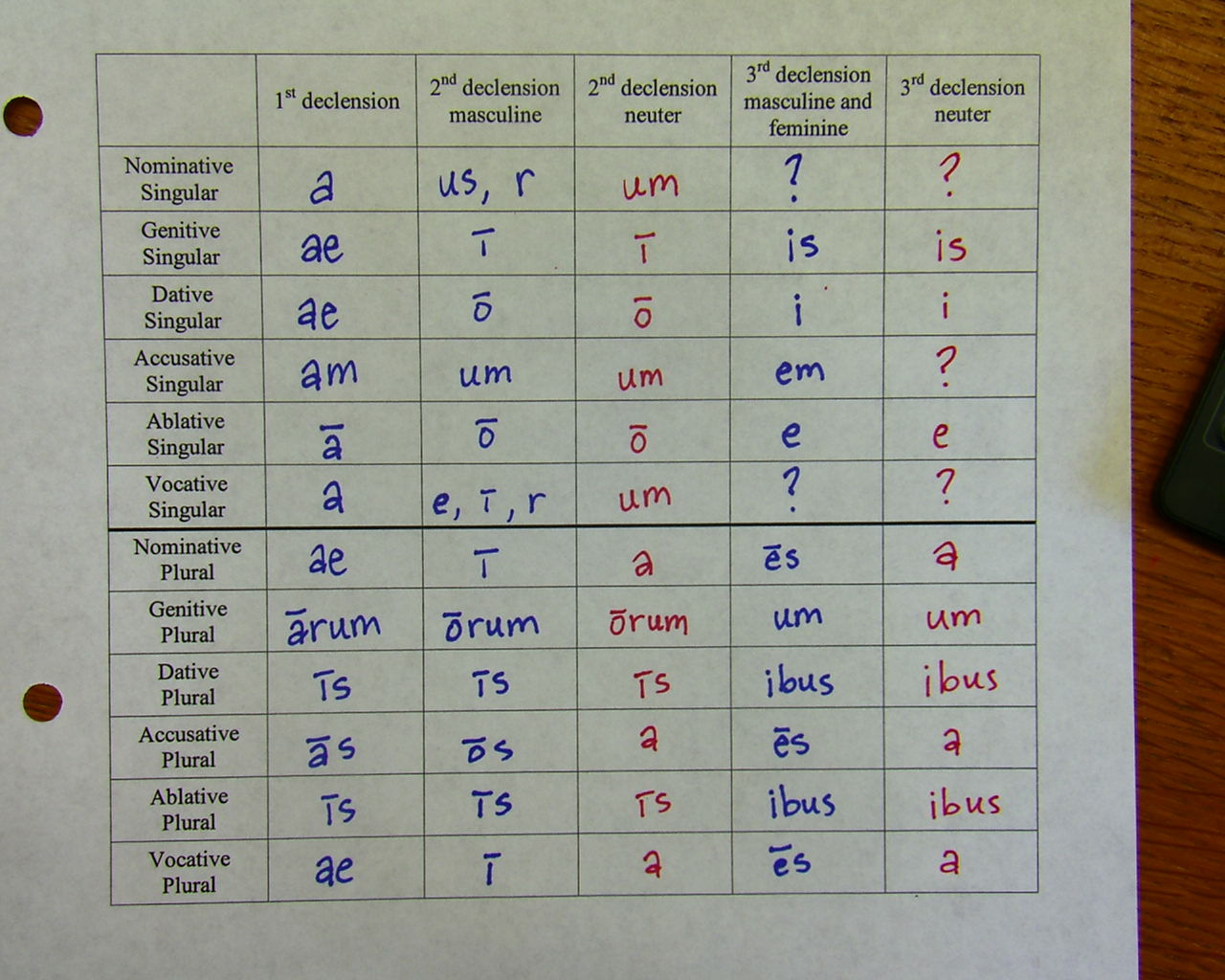
Furthermore, its accusative plural form will most likely end in -is as well. There are six main cases for Latin nouns - nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative and vocative. If a word uses this inflection, the ablative for it is also changed to -i. In rare occasions, the accusative form of the masculine and feminine ĭ-Stem nouns is -im. Examples: mare (sea), portal (portal), templar (templar). All nouns in the third declension ending in -e, -al, and -ar are neuter.Example: pars, partis (pars is only one syllable, it ends in -s, and the “rt” in partis (genitive form) qualifies it as having two consonants prior to the genitive suffix.
Latin noun endings download#
The nominative inflection ends in -x or -s, and two consonants precede the suffix in the genitive form. Download Table Latin noun endings organized by declensions from publication: Inferring Inflection Classes with Description Length We discuss the notion. Or the nominative inflection is monosyllabic (one syllable). While first declension nouns end in '-a', second declension nouns (masculine, since we've dispensed with neuters) usually end in '-us,' '-ius,' or 'er.' Other second declension endings for the nominative are 'ir,' 'ur,' 'os,' 'on,' and 'um.' Greek-based 'Pelion' and 'Andros' are examples of the second declension nouns ending in 'os' and 'on.A word root of a medical term is derived from a Greek or Latin noun or verb. Those groups are separated from one another and categorized according to the letters at the end of their genitive form. The nominative and genitive forms are parisyllabic (meaning they have the same number of syllables). Firstly, prefixes and suffixes, primarily in Greek- but also in Latin.nouns that have the same number of syllables in the genitive and nominative singular some nouns that have a. There are exceptions, but guessing those is a good starting place. Some third declension nouns have the genitive plural ending ‘-ium’. Likewise, a noun ending in -us in the nominative singular is likely Second Declension masculine. The neuter plural forms of -a become -ia.Īn i-Stem third declension noun has one of the following characteristics: Updated on FebruA good bet for a Latin noun whose nominative singular ends in -a is that it is a feminine noun of the First Declension.For all the nouns that have a genitive ending in -ae and which are feminine, we will use the first declension, with the example rosa, rosae, feminine (rose). Bookmark Quiz Bookmark Quiz -/5-RATE QUIZ. Nominative subjects, Vocative function for calling, questioning, Accusative direct objects, Genitive possessive nouns, Dative indirect objects, Ablative prepositional objects. The genitive plural is -ium instead of -um. Latin Noun Endings Can you name the Latin noun endings By oxgu圓.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
